How to Deploy to Google Cloud Run
Google Cloud Run is a managed compute platform that lets you run containers on Google's scalable infrastructure.
This How To guide will show you how to use Docker to deploy your Deno app to Google Cloud Run.
First, we'll show you how to deploy manually, then we'll show you how to automate it with GitHub Actions.
Pre-requisites:
- Google Cloud Platform account
-
dockerCLI installed -
gcloudinstalled
Manual Deployment
Create Dockerfile and docker-compose.yml
To focus on the deployment, our app will simply be a main.ts file that returns
a string as an HTTP response:
import { Application } from "https://deno.land/x/oak/mod.ts";
const app = new Application();
app.use((ctx) => {
ctx.response.body = "Hello from Deno and Google Cloud Run!";
});
await app.listen({ port: 8000 });
Then, we'll create two files -- Dockerfile and docker-compose.yml -- to
build the Docker image.
In our Dockerfile, let's add:
FROM denoland/deno
EXPOSE 8000
WORKDIR /app
ADD . /app
RUN deno cache main.ts
CMD ["run", "--allow-net", "main.ts"]
Then, in our docker-compose.yml:
version: '3'
services:
web:
build: .
container_name: deno-container
image: deno-image
ports:
- "8000:8000"
Let's test this locally by running docker compose -f docker-compose.yml build,
then docker compose up, and going to localhost:8000.
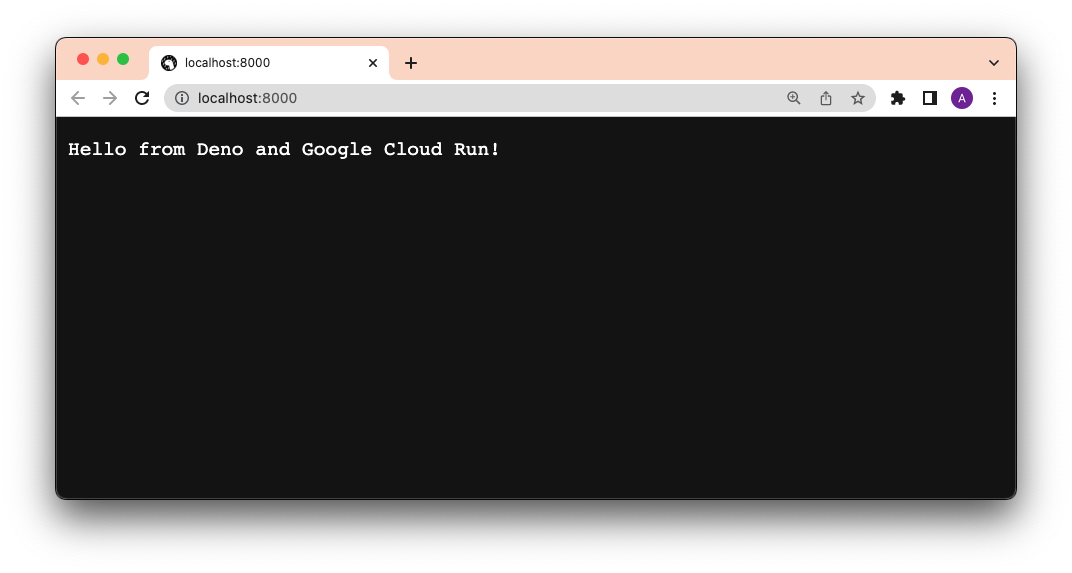
It works!
Set up Artifact Registry
Artifact Registry is GCP's private registry of Docker images.
Before we can use it, go to GCP's
Artifact Registry and click
"Create repository". You'll be asked for a name (deno-repository) and a region
(us-central1). Then click "Create".
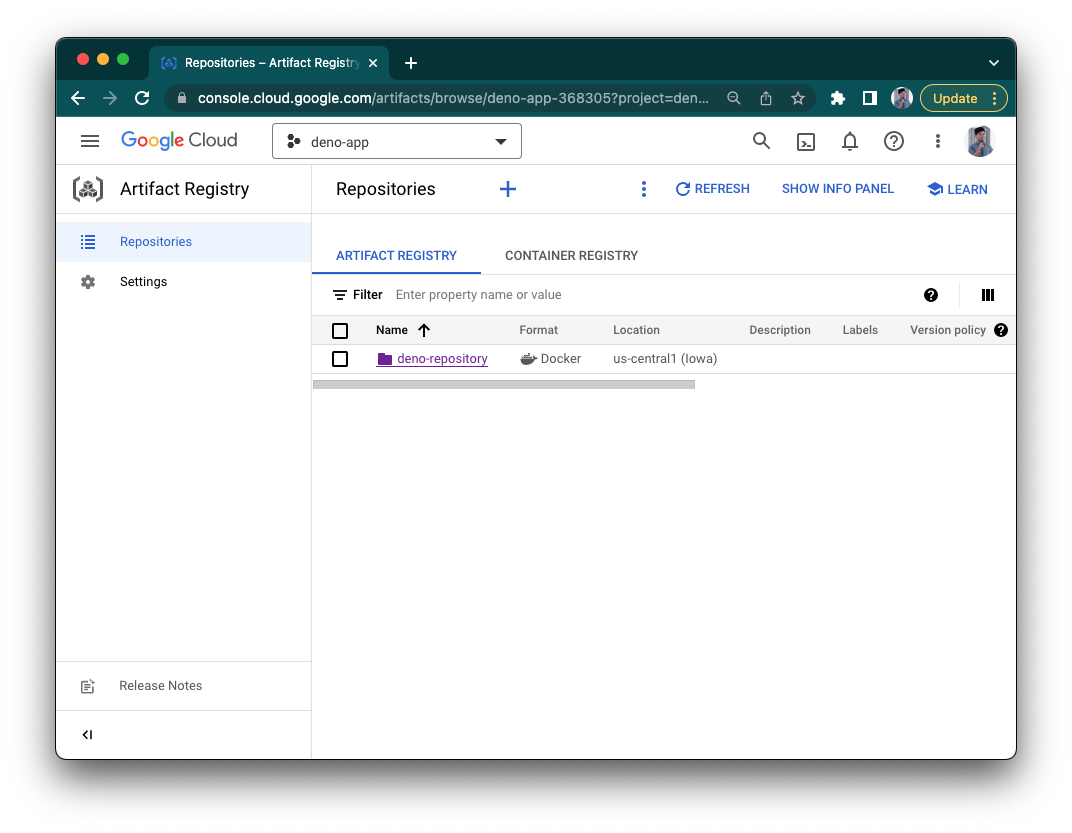
Build, Tag, and Push to Artifact Registry
Once we've created a repository, we can start pushing images to it.
First, let's add the registry's address to gcloud:
gcloud auth configure-docker us-central1-docker.pkg.dev
Then, let's build your Docker image. (Note that the image name is defined in our
docker-compose.yml file.)
docker compose -f docker-compose.yml build
Then, tag it with
the new Google Artifact Registry address, repository, and name. The image name
should follow this structure:
{{ location }}-docker.pkg.dev/{{ google_cloudrun_project_name }}/{{ repository }}/{{ image }}.
docker tag deno-image us-central1-docker.pkg.dev/deno-app-368305/deno-repository/deno-cloudrun-image
If you don't specify a tag, it'll use :latest by default.
Next, push the image:
docker push us-central1-docker.pkg.dev/deno-app-368305/deno-repository/deno-cloudrun-image
More info on how to push and pull images to Google Artifact Registry .
Your image should now appear in your Google Artifact Registry!
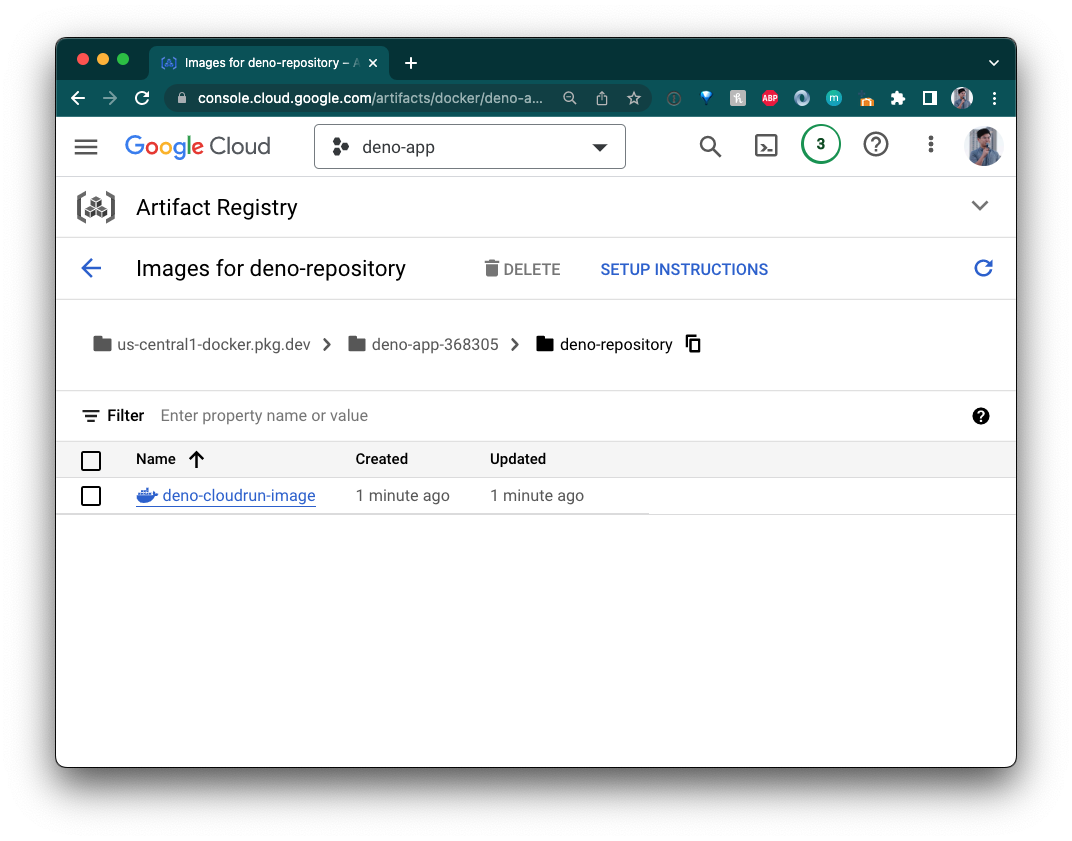
Create a Google Cloud Run Service
We need an instance where we can build these images, so let's go to Google Cloud Run and click "Create Service".
Let's name it "hello-from-deno".
Select "Deploy one revision from an existing container image". Use the drop down
to select the image from the deno-repository Artifact Registry.
Select "allow unauthenticated requests" and then click "Create service". Make
sure the port is 8000.
When it's done, your app should now be live:
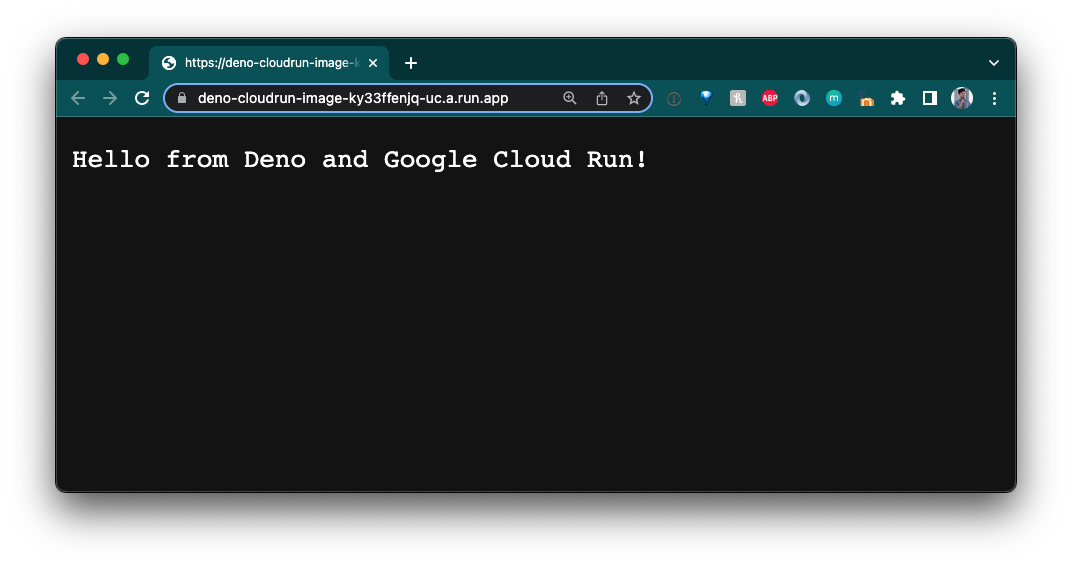
Awesome!
Deploy with gcloud
Now that it's created, we'll be able to deploy to this service from the gcloud
CLI. The command follows this structure:
gcloud run deploy {{ service_name }} --image={{ image }} --region={{ region }} --allow-unauthenticated.
Note that the image name follows the structure from above.
For this example, the command is:
gcloud run deploy hello-from-deno --image=us-central1-docker.pkg.dev/deno-app-368305/deno-repository/deno-cloudrun-image --region=us-central1 --allow-unauthenticated

Success!
Automate Deployment with GitHub Actions
In order for automation to work, we first need to make sure that these both have been created:
- the Google Artifact Registry
- the Google Cloud Run service instance
(If you haven't done that, please see the section before.)
Now that we have done that, we can automate it with a GitHub workflow. Here's the yaml file:
name: Build and Deploy to Cloud Run
on:
push:
branches:
- main
env:
PROJECT_ID: {{ PROJECT_ID }}
GAR_LOCATION: {{ GAR_LOCATION }}
REPOSITORY: {{ GAR_REPOSITORY }}
SERVICE: {{ SERVICE }}
REGION: {{ REGION }}
jobs:
deploy:
name: Deploy
permissions:
contents: 'read'
id-token: 'write'
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- name: CHeckout
uses: actions/checkout@v3
- name: Google Auth
id: auth
uses: 'google-github-actions/auth@v0'
with:
credentials_json: '${{ secrets.GCP_CREDENTIALS }}'
- name: Login to GAR
uses: docker/login-action@v2.1.0
with:
registry: ${{ env.GAR_LOCATION }}-docker.pkg.dev
username: _json_key
password: ${{ secrets.GCP_CREDENTIALS }}
- name: Build and Push Container
run: |-
docker build -t "${{ env.GAR_LOCATION }}-docker.pkg.dev/${{ env.PROJECT_ID }}/${{ env.REPOSITORY }}/${{ env.SERVICE }}:${{ github.sha }}" ./
docker push "${{ env.GAR_LOCATION }}-docker.pkg.dev/${{ env.PROJECT_ID }}/${{ env.REPOSITORY }}/${{ env.SERVICE }}:${{ github.sha }}"
- name: Deploy to Cloud Run
id: deploy
uses: google-github-actions/deploy-cloudrun@v0
with:
service: ${{ env.SERVICE }}
region: ${{ env.REGION }}
image: ${{ env.GAR_LOCATION }}-docker.pkg.dev/${{ env.PROJECT_ID }}/${{ env.REPOSITORY }}/${{ env.SERVICE }}:${{ github.sha }}
- name: Show Output
run: echo ${{ steps.deploy.outputs.url }}
The environment variables that we need to set are (the examples in parenthesis are the ones for this repository)
PROJECT_ID: your project id (deno-app-368305)GAR_LOCATION: the location your Google Artifact Registry is set (us-central1)GAR_REPOSITORY: the name you gave your Google Artifact Registry (deno-repository)SERVICE: the name of the Google Cloud Run service (hello-from-deno)REGION: the region of your Google Cloud Run service (us-central1)
The secret variables that we need to set are:
GCP_CREDENTIALS: this is the service account json key. When you create the service account, be sure to include the roles and permissions necessary for Artifact Registry and Google Cloud Run.
Check out more details and examples of deploying to Cloud Run from GitHub Actions.
For reference: https://github.com/google-github-actions/example-workflows/blob/main/workflows/deploy-cloudrun/cloudrun-docker.yml
 Deno 中文文档
Deno 中文文档